enzyme-gravimetric method|Development and Evolution of Methods Used to Extract and : purchaser The principles of the method are the same as those for the AOAC dietary fiber methods 985.29 and 991.42, Including the use of the same 3 enzymes (heat-stable α-amylase, protease, and amyloglucosldase) and similar enzyme Incubation conditions. Resultado da 6 de abr. de 2020 · Heitengo Futarikiri no Salon de. (Crazy Over His Fingers)? Find out more with MyAnimeList, the world's most active online .
{plog:ftitle_list}
WEBUnidade Jabaquara. Rua Farjalla Koraicho, 51. Ver mais. Nossos diferenciais. Desfrute de tudo que preparamos! Atendimento Humanizado. Preços que cabem no seu bolso. .
Enzymes employed had to meet specific activity requirements and be devoid of contaminating enzymes active on dietary fibre components. The .Two general types of methods have been developed for isolating and analyzing dietary fiber: enzymatic-gravimetric and enzymatic-chemical. The food components isolated vary .This method extends the capabilities of the previously adopted AOAC Official Method 2009.01, Total Dietary Fiber in Foods, Enzymatic-Gravimetric-Liquid Chromatographic Method, applicable to plant material, foods, and food ingredients consistent with CODEX Definition 2009, including naturally occurring, isolated, modified, and synthetic polymers .
plant vochtmeter
The principles of the method are the same as those for the AOAC dietary fiber methods 985.29 and 991.42, Including the use of the same 3 enzymes (heat-stable α-amylase, protease, and amyloglucosldase) and similar enzyme Incubation conditions. Modified enzymatic-gravimetric method (McCleary method) (AOAC 2009.01 (AOAC, 2012), 2011.25 (AOAC, 2011) As for enzymatic-gravimetric method, above, but including non-digestible carbohydrates with three or more monomeric units (intrinsic and added components). SR- Legacy (Haytowitz et al., 2018) FoodData Central (U.S. Department of . This method extends the capabilities of the previously adopted AOAC Official Method 2009.01, Total Dietary Fiber in Foods, Enzymatic–Gravimetric– Liquid Chromatographic Method, applicable to plant material, foods, and food ingredients consistent with CODEX Definition 2009, including naturally occurring, isolated, modified, and synthetic .A collaborative study was conducted on an enzymatic-gravimetric method for determination of total dietary fiber in foods, in which soluble fiber and insoluble fiber are determined separately. Ten collaborators analyzed blind duplicate test samples .
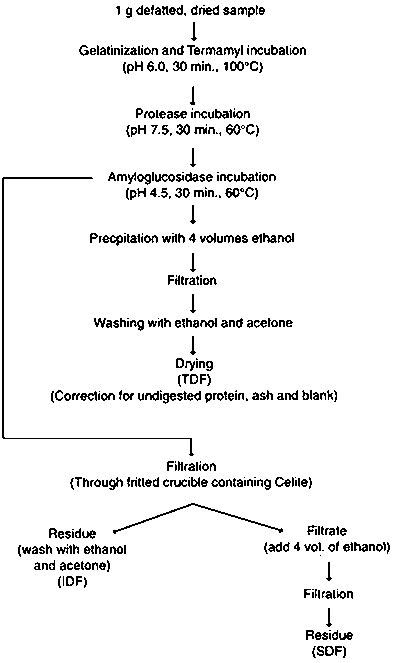
The AOAC 991.43 method (AOAC, 1999) uses three enzymes to hydrolyse samples under different conditions: a heat-stable α-amylase; a protease; and an amyloglucosidase (all enzymes, Cat N° 112979; Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany). The dietary fibre fractions were obtained as the indigestible residues after this enzymatic digestion to .
AOAC Official Method 2011.25 Insoluble, Soluble, and Total Dietary Fiber in Foods Enzymatic-Gravimetric-Liquid Chromatography First Action 2011 [Applicable to plant material, foods, and food ingredients consistent with CODEX Alimentarius Commission . combined action of the two enzymes. The reaction is terminated by pH adjustment and temporary .Digestion of samples under the conditions of AOAC Method 2002.02 followed by the isolation and gravimetric procedures of AOAC Methods 985.29 and 991.43 results in quantitation of HMWDF. The filtrate from the quantitation of HMWDF is concentrated, deionized, concentrated again, and analyzed by LC to determine the LMWSDF, i.e., all nondigestible . OMA 2022.01 is a robust and reproducible method for the analysis of insoluble, soluble (SDFP and SDFS), and TDF in a wide range of matrixes. . Soluble, and Total Dietary Fiber in Foods Using a Rapid Integrated Procedure of Enzymatic-Gravimetric-Liquid Chromatography: First Action 2022.01 J AOAC Int. 2022 Dec 22;106(1):127-145. doi: 10.1093 .
Abstract. A broad range of AOAC Official Methods of Analysis SM (OMA) have been developed and approved for the measurement of dietary fiber (DF) and DF components since the adoption of the Prosky method (OMA 985.29). OMA 985.29 and other OMA were developed to support the Trowell definition of DF. However, these methods do not measure .This method measures the polydextrose content of foods. Polydextrose is a 1 kcal/g randomly bonded polysaccharide used as a food ingredient, and has physiological benefits consistent with dietary fiber. The value obtained from this polydextrose assay may be added to the values from the enzyme-gravimetric methods without concern for double counting.The porosity and surface available for bacteria or molecular probes such as enzymes will depend on the architecture . ethanol concentration from 76% to 41–56% for the precipitation of soluble dietary fibre in the AOAC enzymatic-gravimetric method 985.29. The reduction in ethanol volume for determining the TDF of raw collard, mustard .DOI: 10.1093/JAOAC/75.3.395 Corpus ID: 128658872; Determination of total, soluble, and insoluble dietary fiber in foods: enzymatic-gravimetric method, MES-TRIS buffer: collaborative study
Most gravimetric methods for total dietary fiber (TDF) determination require the complete removal of starch and the partial removal of protein with various combination of enzymes In buffers at different pH values and at temperatures much above ambient condition. A hydrolysis step Is crucial In dietary fiber analysis of samples, such as cereals .
This method extends the capabilities of the previously adopted AOAC Official Method 2009.01, Total Dietary Fiber in Foods, Enzymatic-Gravimetric-Liquid Chromatographic Method, applicable to plant . This enzymatic-gravimetric method was developed by Prosky et al., and it measures the TDF in dried and defatted samples with enzyme hydrolysis using three enzymes: . Among the three enzymes used in both methods, α-amylase hydrolyses the α-1,4 glycosidic bonds of α-linked polysaccharides, such as starch-yielding shorter chains, e.g . Dietary fiber results obtained through the enzymatic–gravimetric method are reliable, considering the accuracy, precision and linearity obtained for cracker biscuits. The fiber values found in the analytical quality control of the FAPAS demonstrated that the method in question shows a satisfactory score, i.e., the values are within the .
A method for measurement of total dietary fiber (TDF) has been validated. This method is applicable to plant materials, foods, and food ingredients as consumed, consistent with the 2009 CODEX definition (ALINORM 09/32/REP), and measures insoluble dietary fiber (IDF) and soluble dietary fiber (SDF), comprising SDF that precipitates in the presence of 78% ethanol (SDFP) .
The chief differences found among the known enzymatic–gravimetric methods regard analysis conditions such as the enzymes employed and the time and temperature of the reaction Mattos, 1997, Lee et al., 1992 introduced changes in AOAC's enzymatic–gravimetric method with the purpose of reducing analysis time and improving the method's .Two methods (an AOAC and a simplified enzymatic-gravimetric method) were used to analyze seven types of canned legumes and eight cooked legumes. Total dietary fiber (TDF) of the canned products ranged between 17% and 23% (dry basis) for chick peas,
Enzymatic gravimetric methods date back to the 19th century. In the 1930s, McCance et al. measured total unavailable carbohydrates in fruits, nuts, and vegetables by determining the residue insoluble in 80% ethanol. This was corrected for starch measured after enzymatic hydrolysis with taka-diastase and for protein. Similar procedures have been . The enzymatic-gravimetric methods AOAC 2009.01 (McCleary et al., 2010) . The AOAC 2011.25 and 991.43 methods use different enzymes, as well as different times and temperatures for incubation (Lee et al., 1992, McCleary et al., 2012). These factors may have affected the SDF quantification, resulting in final values with significant differences. The goal of this work was to evaluate changes in dietary fiber measured by the traditional enzymatic-gravimetric method (AOAC 991.43) and the more recently accepted modified enzymatic-gravimetric method (AOAC 2011.25), mono- and disaccharides, and starch as a function of assessed ripeness in a controlled study of a single lot of bananas and in .Total Dietary Fibre (Applicable Enzymatic-Gravimetric Method to determination of total fibre in cereals, beans, vegetables and fruits) AOAC 992.16 etc . Test for enzyme purity every half yearly β-Glucan (barley gum) β-Glucanase 0.1 95-100 Casein Protease 0.3 0-2 Corn Starch Amylase 1.0 0-2
The gravimetric method, or the gravimetry, is a technique to determine the hydrogen sorption isotherm at equilibrium state via mass measurement [18].Basically in gravimetry, the pressure is changed in steps, and the hydrogen sorption can be characterized by measuring the mass change of a sample during hydrogenation.A simplified enzymatic-gravimetric method for total dietary fiber (TDF) determination has been published and used in the Food Composition Laboratory of the U.S. Department of Agriculture since 1988. THis method gives comparable results to AOAC Official Methods 985.29 and 991.43 but the AOAC methods .AOAC Official Methods SM 985.29, 991.43, 2001.03, and 2002.02, the method quantitates high- and low-molecular-weight dietary fiber (HMWDF and LMWDF, respectively). In 2007, McCleary described a method of extended enzymatic digestion at 37 C to simulate human intestinal digestion followed by gravimetric isolation and quantitation of HMWDF and
vochtmeter blokker
Dietary Fibre and Resistant Starch Analysis
vochtmeter huren gamma
Development and Evolution of Methods Used to Extract and
Determination of total dietary fibre and available
Instagram
enzyme-gravimetric method|Development and Evolution of Methods Used to Extract and